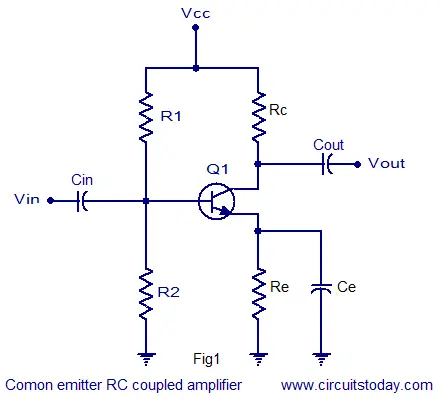
Solved Consider Common Emitter Amplifier Circuit Below U Circuit Diagram A 0.05 volt signal in the input circuit (emitter-to- base in Q 1) has controlled a 2.5 volt signal in the output (emitter-to-collector in Q 1). This is amplification. Figure 3. Relationship of an output signal and ac signal across R 1. You May Also Read: Transistor as an Amplifier: Working & Circuit | NPN Transistor Amplifier; Computing Gain A transistor in which the emitter terminal is made common for both the input and the output circuit connections is known as common emitter configuration. When this configuration is provided with the supply of the alternating current (AC) and operated in between the both positive and the negative halves of the cycle in order to generate the In this case if we applied the input signal of 0 degree phase then output will be obesrved to be Phase of 180 degree. The common-emitter amplifier design is called an inverting amplifier. Examples. Q1. The output resistance of a common base transistor amplifier is 100 kΩ, while the input resistance is 10 Ω. One kΩ is the collector load.
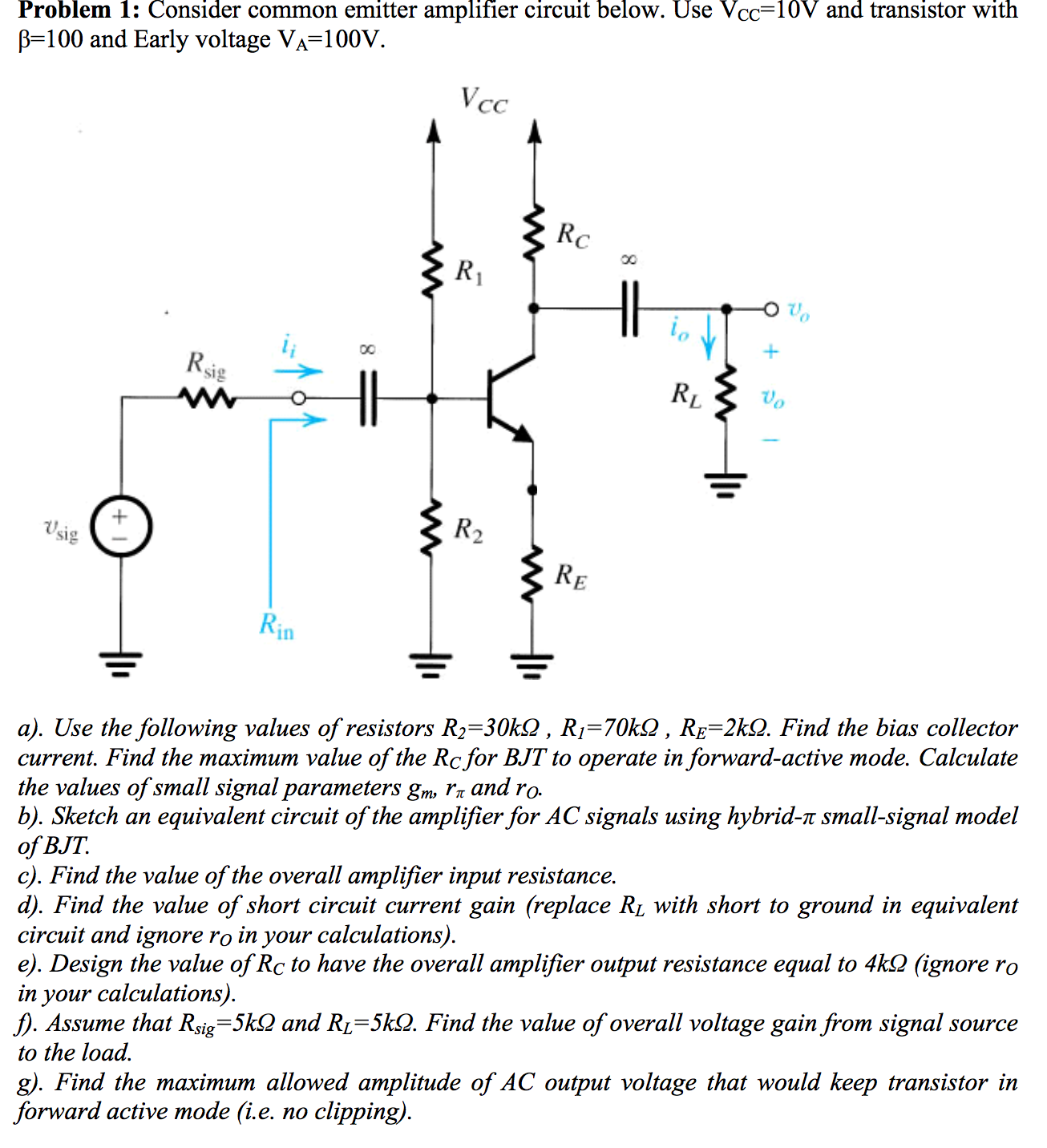
To make them work for amplifying AC signals, the input signal must be offset with a DC voltage to keep the transistor in its active mode throughout the entire cycle of the wave. The current gain of a common-emitter transistor amplifier with the load connected in series with the collector is equal to β. The voltage gain of a common-emitter There are different types of transistor amplifiers operated by using an AC signal input. This is interchanged between the positive value and negative value, hence this is the one way of presenting the common emitter amplifier circuit to function between two peak values. This process is known as the biasing amplifier and it is an important amplifier design to establish the exact operating point

Common Emitter Amplifier : Working and Its Applications Circuit Diagram
The single stage common emitter amplifier circuit shown above uses what is commonly called "Voltage Divider Biasing". This type of biasing arrangement uses two resistors as a potential divider network across the supply with their center point supplying the required Base bias voltage to the transistor. Transistor amplifiers are used frequently in RF (radio frequency), OFC (optic fibre communication), audio amplification, etc. In this lesson, we will discuss how a transistor works as an amplifier. Common-Emitter Configuration. For a transistor to work as an amplifier, we usually use the common-emitter configuration.
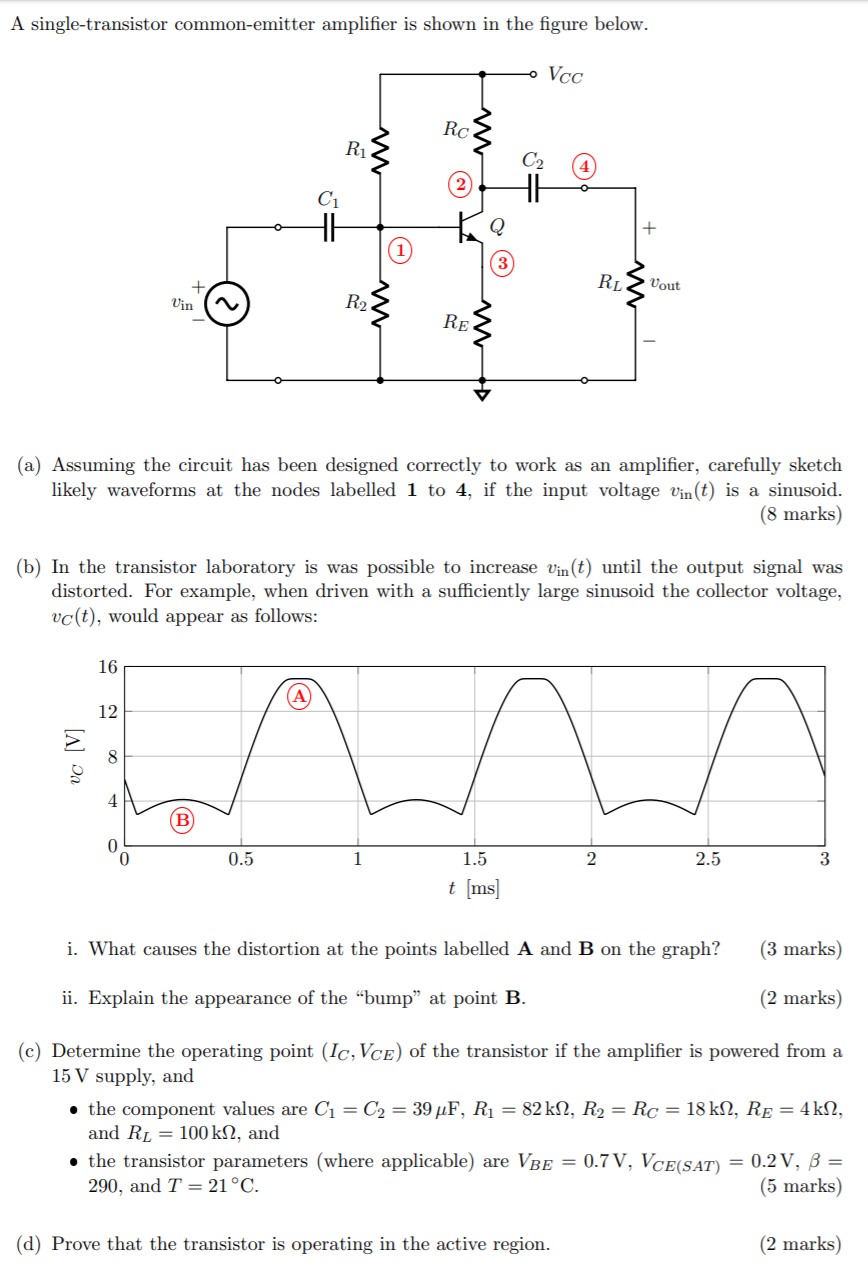
In Common Emitter configuration, emitter terminal is taken as common for both input and output. So input is given between base and the emitter terminals and output is taken between collector and emitter terminals. This is the most commonly used configuration. Circuit diagram of Common Emitter NPN and PNP Transistor:

Common Emitter configuration, Input and Output Characteristics Circuit Diagram
Key learnings: Common Emitter Amplifier Definition: A common emitter amplifier is a transistor configuration where the emitter is grounded, and the input signal is applied to the base.; Working Principle: In a common emitter amplifier, a small change in the base current causes a large change in the collector current, amplifying the input signal.; Phase Shift: The amplifier causes a 180-degree